前言
OkHttp的连接池管理部分也是其核心部分,通过维护连接池,最大限度重用现有连接,减少网络连接的创建开销,以此提升网络请求效率。
连接池实现背景
keep-alive机制
在HTTP1.0中HTTP的请求流程如下:

这种方法的好处是简单,各个请求互不干扰。但在复杂的网络请求场景下这种方式几乎不可用。例如:浏览器加载一个HTML网页,HTML中可能需要加载数十个资源,典型场景下这些资源中大部分来自同一个站点。按照HTTP1.0的做法,这需要建立数十个TCP连接,每个连接负责一个资源请求。创建一个TCP连接需要3次握手,而释放连接则需要4次挥手。重复的创建和释放连接极大地影响了网络效率,同时也增加了系统开销。
为了有效地解决这一问题,HTTP / 1.1提出了keep-alive机制,当一个HTTP请求的数据传输结束后,TCP连接不立即释放,如果此时有新的HTTP请求,且其请求的Host同上次请求相同,则可以直接复用未释放TCP连接,从而省去了TCP的释放和再次创建的开销,减少了网络延时。
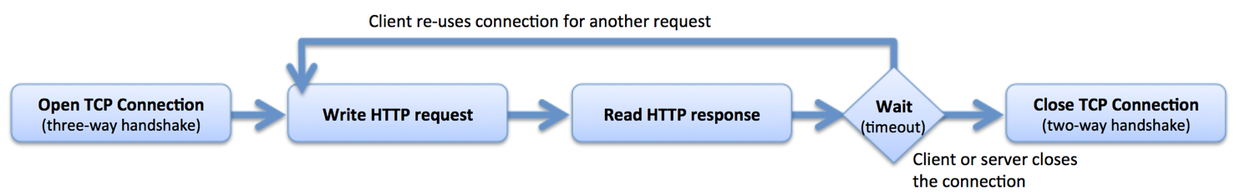
在现代浏览器中,一般同时开启6~8个keep-alive connection的socket连接,并保持一定的链路生命,当不需要时再关闭。而在服务器中,一般是由软件根据负载情况(比如FD最大值、Socket内存、超时时间、栈内存、栈数量等)决定是否主动关闭。
多路复用机制
在HTTP / 1.x中,如果客户端向发起多个并行请求必须建立多个TCP连接,这无疑增大了网络开销。另外,HTTP / 1.x不会压缩请求和响应报头,导致了不必要的网络流量;HTTP / 1.x不支持资源优先级导致底层TCP连接利用率低下。而这些问题都是HTTP / 2要着力解决的。简单来说HTTP / 2主要解决了以下问题:
- 报头压缩:HTTP / 2使用HPACK压缩格式压缩请求和响应报头数据,减少了不必要的流量开销
- 请求与响应复用:HTTP / 2通过引入新的二进制分帧层实现了完整的请求和响应复用,客户端和服务器可以将HTTP消息分解为互不依赖的帧,然后交错发送,最后再在另一端将其重新组装
- 指定数据流优先级:将HTTP消息分解为很多独立的帧之后,我们就可以复用多个数据流中的帧,客户端和服务器交错发送和传输这些帧的顺序就成为关键的性能决定因素。为了做到这一点,HTTP / 2标准允许每个数据流都有一个关联的权重和依赖关系
- 流控制:HTTP / 2提供了一组简单的构建块,这些构建块允许客户端和服务器实现其自己的数据流和连接级流控制
HTTP / 2所有性能增强的核心在于新的二进制分帧层,它定义了如何封装HTTP消息并在客户端与服务器之间进行传输。
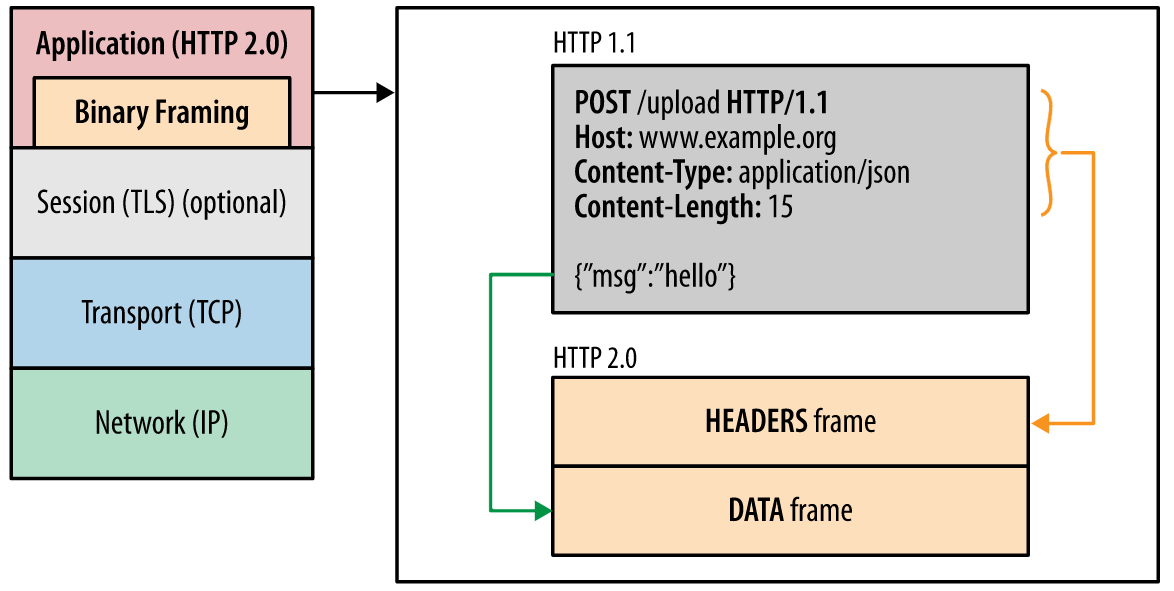
同时HTTP / 2引入了三个新的概念:
- 数据流:基于TCP连接之上的逻辑双向字节流,对应一个请求及其响应。客户端每发起一个请求就建立一个数据流,后续该请求及其响应的所有数据都通过该数据流传输
- 消息:一个请求或响应对应的一系列数据帧
- 帧:HTTP / 2的最小数据切片单位
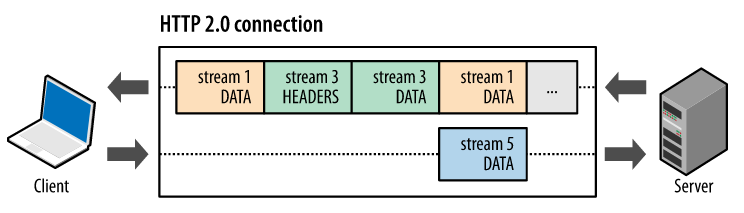
上述概念之间的逻辑关系:
- 所有通信都在一个TCP连接上完成,此连接可以承载任何数量的双向数据流
- 每个数据流都有一个唯一的标识符和可选的优先级信息,用于承载双向消息
- 每条消息都是一条逻辑HTTP消息(例如请求或响应),包含一个或多个帧
- 帧是最小的通信单位,承载着特定类型的数据,例如HTTP标头、消息负载,等等。来自不同数据流的帧可以交错发送,然后在根据每个帧头的数据流标识符重新组装
- 每个HTTP消息被分解为多个独立的帧后可以交错发送,从而在宏观上实现了多个请求或响应并行传输的效果。这类似与多线程环境下的时间片机制
连接池的使用与分析
无论是HTTP / 1.1的keep-alive机制还是HTTP / 2的多路复用机制,在实现上都需要引入连接池来维护网络连接。接下来看下OkHttp中的连接池实现。
OkHttp内部通过ConnectionPool来管理连接池,首先来看下ConnectionPool的主要成员:
|
|
- Call:对Http请求的封装
- Connection / RealConnection:物理连接的封装,其内部有List < Reference < StreamAllocation > > 的引用计数
- StreamAllocation:OkHttp中引入了RealConnection负责管理一个连接上,同时在connection中也通过一个StreamAllocation的引用列表来管理一个连接的流,从而使得连接与流之间解耦。
- connections:Deque双端队列,用于维护连接的容器
- routeDatabase:用来记录连接失败的Route的黑名单,当连接失败的时候就会把失败的路线加进去
ConnectionPool实例化过程
一个OkHttpClient只包含一个ConnectionPool,其实例化过程也在OkHttpClient的实例化过程中实现,ConnectionPool各个方法并没有被直接对外暴露,而是通过OkHttpClient的Internal接口统一对外暴露。
|
|
连接池维护
ConnectionPool内部通过一个双端队列(dequeue)来维护当前所有连接,主要涉及的操作包括:
- put:放入新连接
- get:从连接池中获取连接
- evictAll:关闭所有连接
- connectionBecameIdle:连接变空闲后调用清理线程
- deduplicate:清除重复的多路复用线程
StreamAllocation.findConnection
StreamAllocation在其findConnection方法内部通过调用get方法为其找到stream合适的连接,如果没有则新建一个连接。首先来看一下findConnection的逻辑。
|
|
其主要逻辑大致分为以下几个步骤:
- 查看当前streamAllocation是否有之前已经分配过的连接,有则直接使用
- 从连接池中查找可复用的连接,有则返回该连接
- 配置路由,配置后再次从连接池中查找是否有可复用连接,有则直接返回
- 新建一个连接,并修改其StreamAllocation标记计数,将其放入连接池中
- 查看连接池是否有重复的多路复用连接,有则清除
ConnectionPool.get
接下来再来看get的源码。
|
|
其逻辑比较简单,遍历当前连接池,如果有符合条件的连接则修改标记计数,然后返回。主要判断逻辑是connection.isEligible(address, route)代码。
|
|
- 连接没有达到共享上限
- 非host域必须完全一样
- 如果此时host域也相同,则符合条件,可以被复用
- 如果host不相同,在HTTP / 2的域名切片场景下一样可以复用
deduplicate
deduplicate方法主要是针对在HTTP / 2场景下多个多路复用连接清除的场景。如果当前连接是HTTP / 2,那么所有指向该站点的请求都应该基于同一个TCP连接。
|
|
自动回收
连接池中有socket回收,而这个回收是以RealConnection的弱引用List < Reference < StreamAllocation > >是否为0来依据的。ConnectionPool有一个独立的线程cleanupRunnable来清理连接池,其触发时机有两个:
- 当连接池中put新的连接时
- 当connectionBecameIdle接口被调用时
|
|
该死循环实际上是一个阻塞的清理任务,首先进行清理,并返回下次需要清理的间隔时间,然后调用个wait(timeout)进行等待以释放锁与时间片,当等待时间到了后,再次进行清理,并返回下次要清理的间隔时间。
接下里看一下cleanup方法。
|
|
其基本逻辑如下:
- 遍历连接池中所有连接,标记泄漏连接
- 如果被标记的连接满足(空闲socket连接超过5个 & keep-alive时间大于5分钟),就将次连接从Deque中移除,并关闭连接,返回0,也就是将要执行wait(0),提醒立刻再次扫描
- 如果(目前还可以塞下5个连接,但是有可能泄漏的连接即空闲时间即将到达5分钟),就返回次连接即将到期的剩余时间,供下次清理
- 如果(全部都是活跃的连接),就返回默认的keep-alive时间,也就是5分钟后再执行清理
而pruneAndGetAllocationCount负责标记并找到不活跃连接,类似于引用计数法,如果引用全部为空,返回立刻清理。
|
|
小结
OkHttp的连接池通过引用计数 + 标记清理的机制来管理连接池,使得无用连接可以被回收,并保持多个健康的keep-alive连接,这也是OkHttp的连接池能保持高效的关键原因。